Red Report 2025
Malware targeting password stores surged 3X as attackers executed stealthy Perfect Heist scenarios, infiltrating and exploiting critical systems.

METHODOLOGY
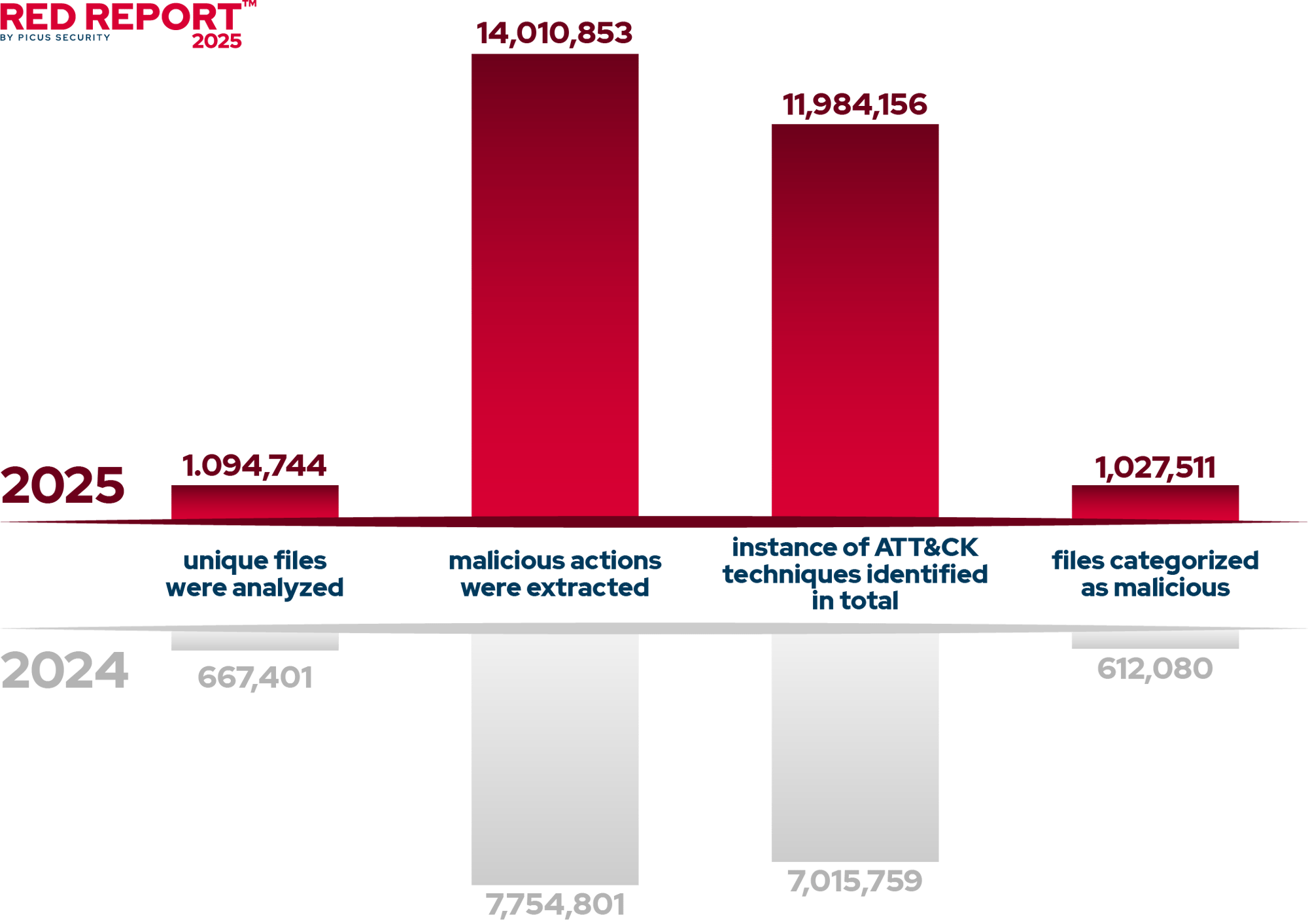
Between January 2024 and December 2024, Picus Labs conducted an extensive analysis of 1,094,744 unique files, of which 1,027,511 (93.86%) were classified as malicious. These files were collected from a diverse range of reliable sources, including commercial and open-source threat intelligence services, security vendors, independent researchers, malware sandboxes, malware databases, and online forums. This comprehensive approach ensured a robust and representative dataset of real-world threats.

Dominance of the Top 10 Techniques:
93% of Malicious Actions Linked to Top Techniques
The top 10 techniques covered 93% of the total malicious activities in 2025 and are headed by T1055 Process Injection, closely followed by T1059 Command and Scripting Interpreter. Other techniques, such as T1555 Credentials from Password Stores and T1071 Application Layer Protocol, now make up parts of the attacks chaining meant to be stealthy and automated while adhering to persistence.


Malware Complexity Reaches New Heights:
14 Malicious Actions per Malware
Malware now does an average of 14 malicious actions and 12 ATT&CK techniques per sample, for a level of sophistication showing a notable increase in the ability of attackers to orchestrate different techniques and methods, thus further increasing the level of complexity needed for detection and defense.
The Rise of Perfect Heists:
Sophistication Meets Coordination
Threats in 2025 are about complex, multistaged, structurally complex attacks-things like "The Perfect Heist" pulled by the SneakThief malware. These are a combination of stealth, automation, and persistence that enables attackers to intrude into network systems, neutralize defenses, exfiltrate sensitive information, and remain hidden for a longer period. The attackers' ability to tailor their tactics to their surroundings speaks to a pivot toward precision-centric campaigns that work to create maximum destruction with minimum exposure.

On demand webinar
Defend Your Enterprise Against
the Infostealer Epidemic
TOP MITRE ATT&CK TECHNIQUES
Previous Picus Red Reports
.png?width=257&height=362&name=Picus-RedReport-2024%20(1).png)
Explore common malware ATT&CK techniques and defend against evasive ‘Hunter-killer’ variants.
.png?width=257&height=362&name=Picus-RedReport-2023%20(1).png)
Discover how lateral movement techniques rose to become the most prevalent adversary tactic.
.png?width=255&height=360&name=Picus-RedReport-2024%201%20(4).png)
Uncover how ransomware became the #1 cyber threat and how to defend against it.
.png?width=256&height=352&name=Picus-RedReport-2020%20(2).png)
Learn about the common ATT&CK techniques and how to prioritize cyber risks.

Every Year I can't wait for the release of the Picus Red Report. This time it's another goodie!
Knowing about the latest trends in malware in the language of MITRE ATT&CK makes it easy to understand and work out what you need to do to protect your organization better.
.png?width=3200&height=323&name=Pattern(1).png)
See the
Picus Security Validation Platform
Request a Demo
Submit a request and we'll share answers to your top security validation and exposure management questions.
Get Threat-ready
Simulate real-world cyber threats in minutes and see a holistic view of your security effectiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions
Between January and December 2024, Picus Labs analyzed 1,094,744 unique files, identifying 1,027,511 (93.86%) as malicious. These files executed 14,010,853 malicious actions, averaging 14 per sample, with 11,984,156 mapped to the MITRE ATT&CK framework. Out of those techniques, we observed the following top 10 techniques being used in the corresponding order: Process Injection, Command and Scripting Interpreter, Credentials from Password Stores, Application Layer Protocol, Impair Defenses, Data Encrypted for Impact, System Information Discovery, Input Capture, Boot or Logon Autostart Execution, and Data from Local System.
Mapping adversaries' TTPs is essential for identifying their attack patterns, including initial access exploits, access control bypass techniques, and other sophisticated methods. By proactively mitigating these security weaknesses—whether through patches, configurations, or other defensive measures—we disrupt the adversary’s kill chain, effectively preventing or delaying their progression. This strategic approach strengthens security posture and reduces the likelihood of a successful breach.
To effectively conduct adversary emulation using the MITRE ATT&CK framework, security teams should first select a threat actor whose tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) align with their organization's threat profile. By mapping these TTPs to the ATT&CK framework, teams can develop detailed emulation plans that replicate the adversary's behavior within a controlled environment. Executing these plans allows organizations to assess their detection and response capabilities against realistic attack scenarios, identify gaps in their defenses, and implement improvements to enhance their overall security posture.
The best way to approach MITRE ATT&CK mapping is to analyze the entire kill chain, from initial access to discovery, credential access, lateral movement, privilege escalation, and impact. The goal is to identify the specific techniques used by the malware or adversary and map each one to the MITRE ATT&CK framework, building a complete picture of the attack. This makes it easier to understand how the attack progresses and where to disrupt it, creating choke points that can stop or slow down the adversary.
Adversaries use info stealer malware to secretly extract sensitive information such as login credentials, financial details, and personal data from compromised systems by leveraging phishing attacks, malicious downloads, and software exploits. Once installed, these malware variants harvest data from browsers, email clients, and stored credentials, often incorporating keylogging and clipboard monitoring. The stolen data is then exfiltrated to attacker-controlled servers via encrypted channels, enabling cybercriminals to use it for financial fraud, identity theft, or to sell on the dark web, posing serious risks to individuals and organizations alike.
Process injection is a technique where attackers execute malicious code within the address space of a legitimate process, allowing them to evade detection and potentially gain elevated privileges. This method enables adversaries to mask their activities under the guise of trusted processes, making it challenging for security systems to identify malicious behavior. To mitigate process injection, organizations should implement application control solutions like AppLocker or Windows Defender Application Control, which prevent unauthorized code execution. Additionally, enabling features such as Windows Defender Exploit Guard's Arbitrary Code Guard and Export Address Filtering can further protect against these attacks. Regular monitoring of process behaviors and employing endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools can also aid in identifying and responding to injection attempts.
.png?width=2000&name=Group%20427319045%20(7).png)