Effortlessly map your detection content to MITRE ATT&CK® using AI-driven analysis to assess your detection coverage.
MITRE ATT&CK® Framework
MITRE ATT&CK® Framework is a knowledge base of real-world adversary tactics and techniques.
Picus uses the MITRE ATT&CK® Framework to simulate real-world techniques, validate your security controls, and reveal the gaps in your detection and prevention capabilities.
.gif?width=1200&height=625&name=Mitre-Table-Gradient%20(2).gif)
How to Operationalize MITRE ATT&CK® with Picus
Our customized heat map helps visualize ATT&CK coverage to demonstrate the prevention and detection efficacy of your controls.
The 14 MITRE ATT&CK® Tactics Explained
Understand the core of the MITRE ATT&CK® Framework with its 14 tactics that represent the stages of an adversary’s attack lifecycle. Learn how each tactic reveals different attacker goals and helps security teams strengthen their defenses.
Tactic |
Description |
Key Techniques |
Why It Matters |
|
Reconnaissance (TA0043) |
Passive or active techniques used to collect information before an attack begins. |
Phishing for Information, Search Open Websites/Domains |
Reconnaissance helps attackers identify entry points, vulnerabilities, and potential targets. |
|
Resource Development (TA0042) |
Adversaries create or acquire tools, infrastructure, and capabilities before launching an attack. |
Obtain Capabilities, Compromise Accounts |
These preparations lay the groundwork for successful and scalable operations. |
|
Initial Access (TA0001) |
Adversaries attempt to gain a foothold in your network by exploiting external-facing systems or targeting users directly. |
Phishing, Drive-by Compromise, Exploit Public-Facing Application |
This is where most attacks begin. Preventing initial access drastically reduces the chance of a breach. |
|
Execution (TA0002) |
The attacker runs malicious code on a local or remote system after gaining access. | Command and Scripting Interpreter, Malicious File Execution | Execution enables adversaries to deploy payloads and advance further into your network. |
|
Persistence (TA0003) |
Tactics that allow attackers to maintain access across reboots, credential resets, or system upgrades. | Boot or Logon Autostart, Scheduled Task/Job | Persistence mechanisms ensure that an attacker can return even after detection or a system reboot. |
|
Privilege Escalation (TA0004) |
Attackers attempt to gain higher-level permissions on a system or domain. | Exploitation for Privilege Escalation, Access Token Manipulation, Process Injection | Elevated privileges allow attackers to access sensitive data and critical systems. |
|
Defense Evasion (TA0005) |
Techniques used to avoid detection by security tools and analysts. | Obfuscated Files or Information, Deactivation of Security Tools, Impair Defenses | Successful defense evasion allows attackers to operate undetected for longer periods. |
|
Credential Access (TA0006) |
Adversaries steal credentials to gain access to systems and services. | Brute Force, Credential Dumping, Credentials from Password Stores | Compromised credentials can give attackers legitimate access, making them harder to detect. |
|
Discovery (TA0007) |
Activities that help attackers map out the environment and identify targets. | System Information Discovery, Account Discovery | Discovery enables lateral movement and targeting of high-value systems. |
|
Lateral Movement (TA0008) |
Attackers move through the network to access additional systems or data. |
Lateral movement expands an attacker’s reach across your organization. |
|
|
Collection (TA0009) |
Adversaries gather information from systems, such as files, credentials, or logs. |
Screen Capture, Data Staged, Input Capture, Data From Local System |
Data collection is a key step before exfiltration or impact actions. |
|
Command and Control (TA0011) |
Adversaries establish communication channels with compromised systems. |
Application Layer Protocol, Encrypted Channel |
Without C2, attackers cannot remotely control systems or receive stolen data. |
|
Exfiltration (TA0010) |
Stolen data is transferred out of the network to an attacker-controlled location. |
Exfiltration Over Web Service, Exfiltration Over C2 Channel |
This is when sensitive data leaves your environment—often triggering major impact or compliance risk. |
|
Impact (TA0040) |
Attackers attempt to disrupt, destroy, or manipulate systems and data. |
Data Destruction, Service Stop, Data Encrypted for Impact |
Impact techniques lead to business disruption, financial losses, and reputational damage. |
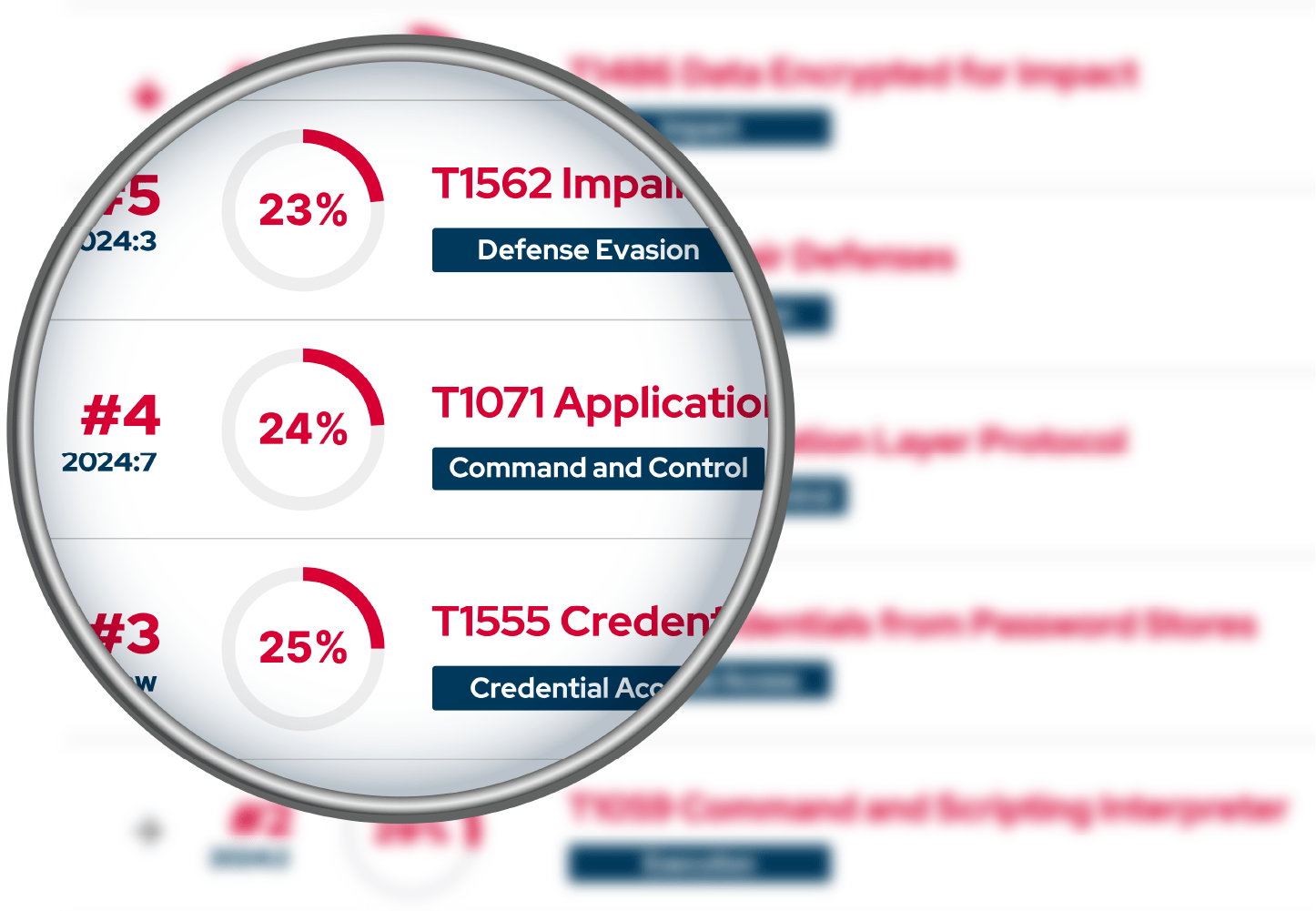
The Red Report 2025
Red Report 2025 connects the dots between MITRE ATT&CK® tactics, techniques, and actual adversary activity.
See which techniques appear most often in real-world campaigns—and use this knowledge to strengthen your posture across all 14 tactics.
Validate Your Security with
MITRE ATT&CK® Mapping
Picus Attack Surface Validation (ASV) |
Picus Security Control Validation (SCV) |
Picus Attack Path Validation (APV) |
Picus Cloud Security Validation (CSV) |
|||||||
Attack Surface Validation |
Endpoint Attacks |
Network Infiltration Attacks |
Web Application Attacks |
E-mail Infiltration Attacks (Phishing Attachment/
|
Data Exfiltration Attacks |
URL
|
Attack Path Validation |
Cloud Security Validation |
||
Vulnerability Exploitation |
Malware Download |
|||||||||
Reconnaissance |
✔ |
|||||||||
Resource Development |
✔ |
|||||||||
Initial Access |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
|||||
Execution |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
||||||
Persistence |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
||||||
Privilege Escalation |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
||||||
Defense Evasion |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
||||||
Credential Access |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
||||||
Discovery |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
|||||
Lateral Movement |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
|||||||
Collection |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
|||||||
Command and Control |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
|||||||
Exfiltration |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
||||||
Impact |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
|||||||
Active Directory Focused
Active Directory is a critical component of many enterprise networks, managing authentication and authorization for users and resources. Due to its central role, it is a prime target for attackers seeking to gain extensive control over network environments. The blog posts below explained adversary techniques used in Active Directory attacks in great detail.






Frequently Asked Questions
The MITRE ATT&CK® framework is a globally accessible and free knowledge base of adversary tactics and techniques.
These techniques are based on real-world observations of adversary behaviors and are created by analyzing actual cyberattacks. MITRE ATT&CK® is a community-driven framework, continuously enriched by contributions from cybersecurity experts around the world. The power of the framework lies in its open nature—anyone can access, use, and contribute to it to improve collective defense.
Organizations can implement the MITRE ATT&CK® framework by validating their security posture against tactics and techniques listed in the ATT&CK framework.
The MITRE ATT&CK® framework helps security teams identify gaps, prioritize defenses, and simulate adversary behaviors based on real-world threat intelligence.
MITRE ATT&CK® outlines adversary behavior through tactics, which represent an attacker’s objectives, and techniques, which describe the methods used to achieve those objectives.
By leveraging open-source threat intelligence reports like the Picus Red Report, security teams can gain deep insights into how attackers may employ these techniques against their organizations.