What Is Security Control Rationalization?
LAST UPDATED ON DECEMBER 27, 2023
The complexity and diversity of security tools utilized in organizations can lead to significant challenges in managing and optimizing their usage. The process of Security Control Rationalization serves to address the optimization issues of organizations’ existing security controls, allowing for better decision-making, improved efficiency, and maximized returns on security investments.
In this blog, we are deep diving into what security control rationalization is, its importance to organizations, and the key steps that it consists of.
What Is Security Control Rationalization?
Security Control Rationalization is a cybersecurity process that involves the systematic evaluation, selection, and optimization of security controls within an organization. It's about ensuring that each security measure in place is necessary, effective, and contributes to the organization's overall security posture in the most efficient way.
Why Is Security Control Rationalization Important?
Security Control Rationalization can help organizations improve their security posture by identifying redundancies and overlaps in their security controls, streamlining their security environment, and making it more efficient and effective. This data-driven approach improves the efficiency and effectiveness of security controls, enhancing the overall cybersecurity posture of an organization.
The importance of security control rationalization can be categorized in three main points.
a. Investment Decision Support
Security Control Rationalization offers data-driven assessments that aid decisions regarding investment or divestment in specific security controls or areas. The emphasis is on the overall effectiveness of security controls, rather than the performance of a single product, fostering more holistic investment decisions.
Furthermore, Security Control Rationalization facilitates strategic decision-making by identifying overlapping security products. In cybersecurity, overlapping security controls can often lead to redundancy, sometimes termed control redundancy. This implies the existence of multiple solutions performing similar tasks. Continuous assessment of the security posture of your systems is vital for managing such overlapping controls. Should two products serve the same purpose, it could be advantageous to retain only the more effective or efficient one.
In summary, Security Control Rationalization enhances the return on security investments by providing a comprehensive view of the functionality of security controls.
b. Security Architecture Rationalization
Security Control Rationalization helps rationalize strategic changes in the security architecture by assessing the impact of those changes. This ensures any alterations to the infrastructure do not compromise the organization's security stance.
c. Product Evaluation and Testing
Security Control Rationalization is a key step in assessing the capabilities and performance of security products during the pre-sales stage. This process equips organizations with valuable insights to discern if these services align with their specific security requirements, thereby enabling informed decisions about potential investments.
How Does Security Control Rationalization Relate to Risk Management?
Security Control Rationalization is an important part of risk management because it helps organizations in four key areas.
-
Identify and mitigate gaps in their security controls:
-
Reduce redundancies in their security controls
-
Make informed investment decisions about security controls
-
Manage changes to their security architecture
Each of these areas are provided with a brief description below.
a. Identifying and Mitigating the Gaps in Security Controls
Security Control Rationalization helps organizations identify gaps in their security controls by comparing their current security controls to a set of best practices or industry standards. This allows organizations to identify areas where they may be at risk and take steps to mitigate those risks.
b. Reducing Redundancies in Security Controls
Security Control Rationalization helps organizations reduce redundancies in their security controls. In cybersecurity, redundancies occur when multiple security controls are designed to address the same risk. This can lead to inefficiencies and increased costs, as organizations may be spending money on controls that are not necessary.
Here are some examples of how Security Control Rationalization can help organizations reduce redundancies in security controls:
-
Step 1: Identify the Overlapping Controls
Security Control Rationalization can help organizations identify their overlapping existing security solutions, allowing organizations to identify controls that are designed to address the same risk.
For instance, an organization may be operating with two distinct firewalls from different vendors, creating a redundant layer. Both firewalls essentially serve the same function of preventing unauthorized access and attacks. Through the process of Security Control Rationalization, such redundancies can be recognized and addressed.
In another scenario, a company might be employing two different encryption tools to secure its data at rest. This redundancy means that two tools are doing the same job, which can lead to unnecessary complexity and cost. Using Security Control Rationalization, the organization can determine these overlapping controls and decide on the optimal solution based on factors such as efficiency, cost, and effectiveness.
Likewise, an organization might use both a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tool and a log management tool that perform similar tasks, such as collecting, analyzing, and storing log files. Security Control Rationalization can assist in recognizing this overlap, enabling the organization to choose the more effective tool and streamline its security operations.
By implementing Security Control Rationalization, organizations can eliminate these unnecessary redundancies, improve security control effectiveness, and optimize their resource allocation.
-
Step 2: Eliminating Unnecessary Controls
Once overlapping security controls have been identified, Security Control Rationalization can help organizations eliminate those controls that are not necessary. This can save organizations money and improve their security posture by reducing the complexity of their security environment.
-
Step 3: Repurposing Existing Controls
In some cases, it may not be possible to eliminate unnecessary security controls. In these cases, Security Control Rationalization can help organizations repurpose existing controls to address other risks. This can save organizations money and improve their security posture by making more efficient use of their resources.
By following these steps, organizations can reduce redundancies in their security controls and save money and improve their security posture.
c. Informed Investment Decisions
Security Control Rationalization provides organizations with a data-driven assessment of the effectiveness of their security controls. This information can be used to make informed decisions about where to invest in new security controls.
Here are some examples of how Security Control Rationalization can help organizations make informed investment decisions about security controls:
-
Prioritizing Security Controls
Security Control Rationalization can help organizations prioritize their security controls by assessing the effectiveness of each control and the risks it mitigates. This allows organizations to focus their investment on the most important security controls.
-
Evaluating the Cost-Effectiveness of Security Controls
Security Control Rationalization can help organizations evaluate the cost-effectiveness of security controls by assessing the cost of each control and the benefits it provides. This allows organizations to make informed decisions about which security controls are worth the investment.
By following these steps, organizations can make informed investment decisions about security controls and improve their security posture.
d. Managing Changes to Security Architecture
Any changes to an organization's security architecture can introduce new risks.
For example, an organization may be considering implementing a new cloud-based application. Security Control Rationalization can help the organization identify the security risks associated with this change and take steps to mitigate those risks.
In conclusion, Security Control Rationalization is an important part of risk management. It helps organizations to identify and mitigate gaps in their security controls, reduce redundancies in their security controls, make informed investment decisions about security controls, and manage changes to their security architecture.
By implementing Security Control Rationalization, organizations can improve their security posture and protect their assets from cybersecurity threats.
What Are the Key Steps in Security Control Rationalization?
Security control rationalization is the process of reviewing, evaluating, and optimizing an organization's security controls to ensure that they are effective in mitigating risk.
The key steps in security control rationalization can be summarized into four main categories.
-
Assessment
The assessment step involves reviewing all the security controls currently deployed in the organization, including software, hardware, policies, and procedures.
-
Evaluation
The evaluation phase of security control rationalization is critical to ensuring the effectiveness of an organization’s security controls. This phase may involve leveraging security assessment solutions such as vulnerability scanners, penetration testing, red teaming as well as the use of breach and attack simulation (BAS) solutions as a continuous and complementary solution.
BAS solutions simulate real-world attack scenarios to assess how well an organization’s existing security controls are responding to a possible attack. This proactive method enables organizations to identify potential vulnerabilities, understand how well their security controls would hold up against actual threats, and prioritize security enhancements based on actual data and insights.
-
Rationalization
The rationalization step involves determining if each control is necessary and effective, identifying any gaps in your existing security that needs immediate attention, or recognizing any redundancies that could be eliminated. This process often includes a cost-benefit analysis to ensure resources are being utilized efficiently.
-
Optimization
Make changes based on the findings of the rationalization process. Optimizing your security controls could involve implementing new controls, eliminating redundant or ineffective ones, or adjusting the configuration of existing controls to enhance their effectiveness.
In conclusion, Security Control Rationalization is an important process for organizations of all sizes. By following these steps, organizations can ensure that their security controls are effective in mitigating risk and protecting their assets.
What Are the Common Challenges Faced in Security Control Rationalization?
Here are three main challenges that organizations face implementing security control rationalization.
Navigating the Complexity in Security Control Rationalization: The Challenge of Multiple Security Tools
A key challenge faced in Security Control Rationalization is managing the complexity associated with having numerous discrete security tools. According to Panaseer’s Security Leader’s Peer Report, many organizations reportedly run an average of 57 separate security tools, with some running over 76 [1]. This extensive use of different security tools can result in overlaps and gaps in security coverage, making the task of rationalization quite complex.
Uncovering Cybersecurity Performance: Addressing the Evaluation Gap in Security Tool Effectiveness
Additionally, there is a lack of thorough evaluation in terms of how well the cybersecurity tools are performing. Many IT professionals aren't fully aware of the effectiveness of their deployed cybersecurity tools, and a significant proportion don't believe they're getting the most out of their security investments. This lack of understanding and visibility into the performance of security tools can complicate the rationalization process.
Quantitative Data Deficit: The Roadblock to Data-Driven Decision Making
Another challenge is the decision-making process related to investing or divesting in specific areas or security controls. Without a comprehensive understanding and quantitative data on how the security controls function, organizations can struggle to make the right decisions and achieve the best return from their budgets.
Therefore, it can be said that managing the complexity of numerous security tools, lacking understanding and visibility into tool performance, and making informed investment decisions are the common challenges faced in Security Control Rationalization.
How Can Automation Aid in Security Control Rationalization?
Automation, particularly in the form of Breach and Attack Simulation (BAS), can significantly aid in the process of Security Control Rationalization. BAS provides an automated, continuous approach to validating the effectiveness of security controls.
Here is how Breach and Attack Simulation can be beneficial for Security Control Rationalization:
-
Identifying Gaps in Each Security Control
The challenge of Security Control Rationalization is amplified when organizations use a wide variety of security tools. As indicated in Panaseer’s Security Leader’s Peer Report, it's common for organizations to handle an average of 57 separate security tools, with some even juggling more than 76 [1]. This diversity can lead to coverage gaps, making the rationalization process trickier.
Adding to the complexity, traditional security measures, like penetration testing or vulnerability scanning, often can't thoroughly assess each existing solution in an organization. This is where Breach and Attack Simulation (BAS) tools step in. To uncover vulnerabilities in their security posture, organizations can employ a BAS solution to run automated attack simulations against the security solutions they wish to rationalize.
The proactive approach of BAS technologies enables organizations to systematically assess how well their existing security controls respond to different and real-life threat scenarios. The results of these simulations provide clear, quantifiable data on where gaps exist, thereby assisting in rationalizing these security controls.
-
Detecting Overlapping and Redundant Security Controls
When security teams have multiple controls that seem to perform similar functions, it can be challenging to identify overlaps manually. By running Breach and Attack Simulation on each security control individually and comparing the results, teams can precisely measure the effectiveness of each tool.
If the simulations reveal that one tool consistently outperforms the other in the same scenarios, it might be an indication of redundant controls. The lesser-performing tool could be disabled or repurposed, helping organizations optimize their security investments.
In conclusion, the automation offered by Breach and Attack Simulation can greatly streamline and enhance the Security Control Rationalization process. By continually testing security controls and providing a clear, data-driven picture of their effectiveness, BAS allows organizations to make more informed decisions about their security posture and investments.
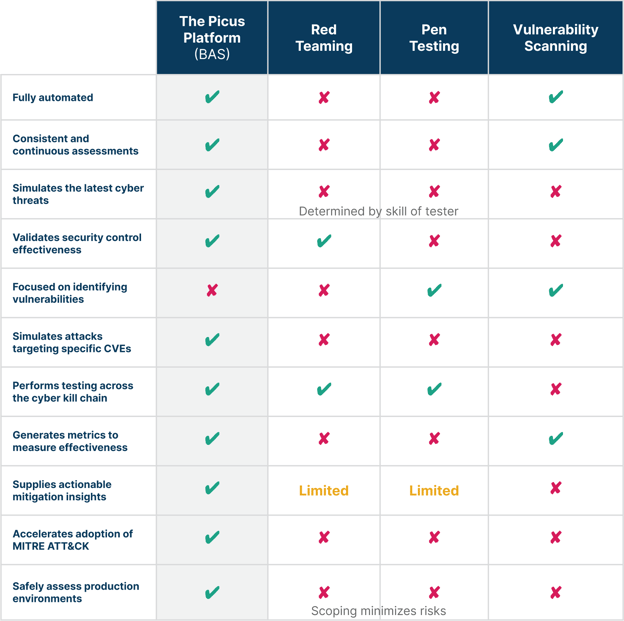
BAS vs. Traditional Security Assessment Solutions
The table below provides a detailed comparison of a Breach and Attack Simulation (BAS) solution to existing security assessment solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How Often Should Security Control Rationalization Be Performed?
Can Security Control Rationalization Help in the Prevention of Data Breaches?
What Is the Impact of Security Control Rationalization on Threat Detection?
How Is Security Control Rationalization Used in Compliance Frameworks?
[1]T. Finnane, “Panaseer 2022 Security Leaders Peer Report,” Panaseer, Nov. 30, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://panaseer.com/reports-papers/report/2022-security-leaders-peer-report/. [Accessed: May 23, 2023]








