Digital Operational Resiliency Act (DORA)
Ensure compliance and reduce risks with adversarial exposure validation.
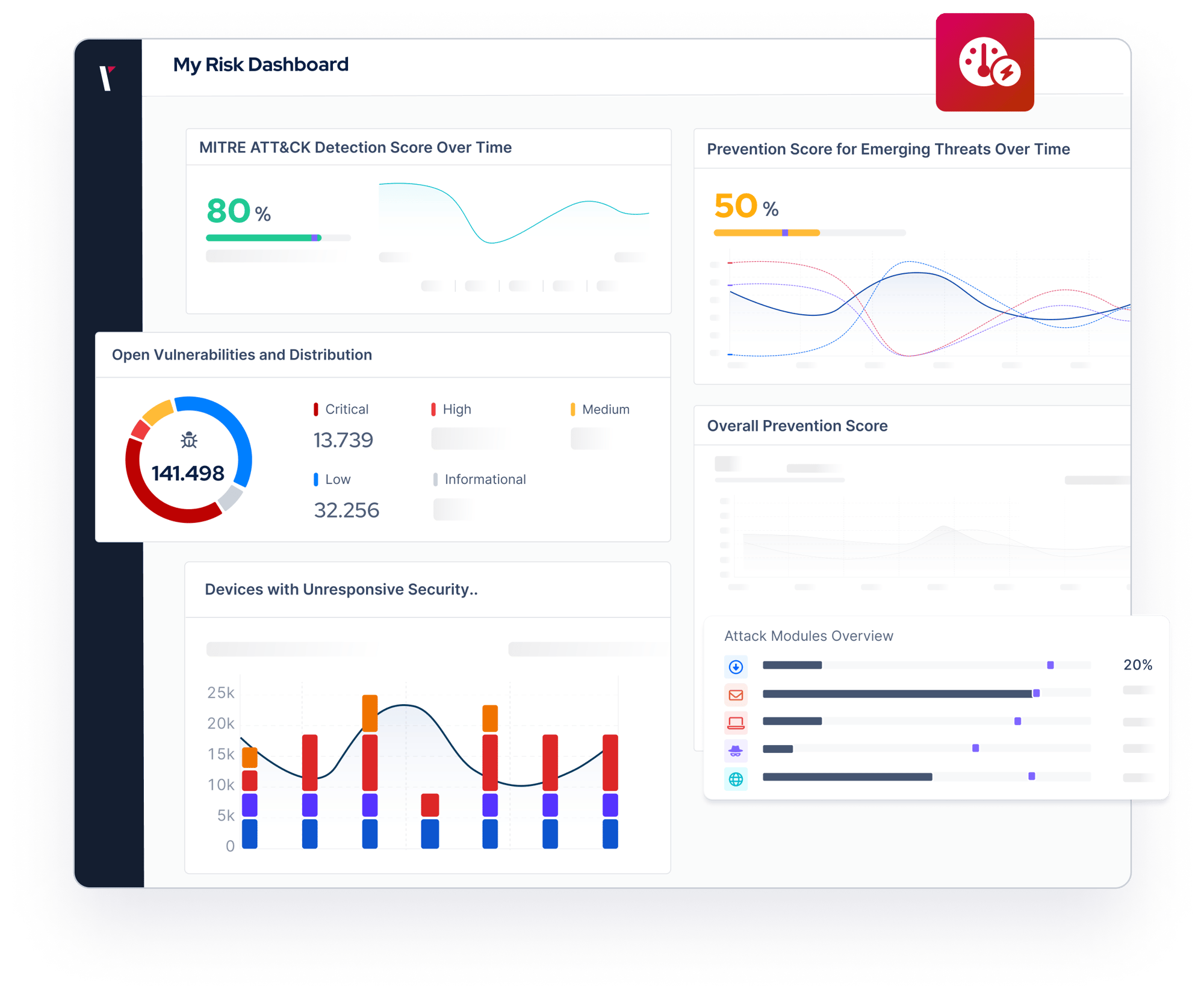
Achieve Regulatory Readiness with Continuous Security Validation
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) sets the standard for financial institutions across the European Union to manage ICT risks, maintain operational continuity, and combat evolving cyber threats. By addressing critical areas such as risk management, incident response, and third-party oversight, DORA establishes a unified standard for digital resilience.
DORA contains five pillars to cover security controls that financial organizations are required to meet to comply.
Benefits of Security Validation for DORA Compliance
Accelerate DORA Compliance with Picus
Watch now and learn:
How Security Validation platforms support compliance
Threat-Led Penetration Testing’s role in securing financial entity critical live production systems
How to accelerate your process, combine and correlate exposure data, and validate security control effectiveness
How to Support DORA Compliance
ICT Risk Management
Financial institutions must have an internal governance and control framework for managing ICT risks. This risk management framework must cover risk identification, protection, detection, response, and recovery.
How to Address the Gap:
- Simulate real-world cyberattacks to assess the efficacy of your security controls, including firewalls, endpoint protection, and intrusion detection systems. Picus ensures your defenses can handle the evolving threats your organization faces, aligning with DORA’s ICT Risk Management pillar.
- Prioritize risk mitigation strategies by mapping simulation results to MITRE ATT&CK® and other frameworks. Picus Security Control Validation (SCV) supplies actionable mitigation recommendations, including vendor-specific prevention signatures and detection rules, to save time and effort.
- Continuously improve your security posture by tracking changes over time, including your security score, device performance, and threats, to maintain and exceed compliance with DORA requirements.
ICT-Related Incident Management
Financial organizations must define, establish, and implement an ICT-related incident management process to detect, manage, and notify ICT-related incidents.
How to Address the Gap:
- Gain a unified view of your assets with Picus Attack Surface Validation (ASV), consolidating vulnerability data and enhancing visibility across your environment.
- Detect non-compliant devices with insufficient security coverage and prioritize vulnerabilities based on the criticality of your assets.
- Simulate ICT-related incidents to refine response workflows, improve reaction times, and get actionable insights to optimize incident handling processes.
Digital Operational Resilience Testing
Institutions must establish a comprehensive digital resilience testing program to identify weaknesses, deficiencies, and gaps in ICT systems.
How to Address the Gap:
- Simulate a range of attack types—phishing, ransomware, insider threats, and more. Adversary Exposure Validation (AEV) tools like Picus Security, which provides Automated Penetration Testing and Breach and Attack Simulation, are central to conducting Threat-Led Penetration Testing (TLPT). With the Picus Platform, organizations can mimic the tactics, techniques, and procedures of genuine threat actors to assess the resilience of critical systems without disrupting operations.
- Map potential attack paths with Picus Attack Path Validation (APV), revealing exploitation steps such as lateral movement and privilege escalation. This ensures critical assets are optimally defended.
- By running comparisons over time of your security score, status of security devices, and threats, organizations can track critical changes affecting security posture and maintain compliance.
Third-Party Risk Management
Organizations must integrate third-party risk management into their overall ICT risk framework. This includes assessing vendors’ security measures and managing potential vulnerabilities external providers introduce.
How to Address the Gap:
- Assess vendor risk by simulating attack scenarios involving third-party environments such as firewalls, SIEM, and EDR to ensure compliance with DORA’s third-party risk management standards.
- Validate the security of your cloud infrastructure with Picus Cloud Security Validation (CSV), including data storage and access controls, to maintain resilience and adherence to industry best practices.
Information Sharing
DORA encourages financial institutions to share cyber threat intelligence, including indicators of compromise and tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs). Collaborative information sharing aims to enhance sector-wide resilience against threats.
How to Address the Gap:
- Get real-time analytics and detailed incident reports to identify vulnerabilities, analyze attack vectors, and enhance your defenses against potential threats.
- Leverage global threat intelligence, customizable scenarios, and industry-specific templates to align your defenses with existing and emerging risks.
- Enable collaboration through internal and external sharing of validated findings, improving resilience and building a stronger, interconnected defense ecosystem.
Reducing Risk in Finance with Exposure Validation
Discover how finance security teams focus on critical risks, reducing immediate vulnerabilities as attack surfaces rapidly expand.

Adversarial Exposure Validation is Essential
As the leading adversarial exposure validation solution, Picus Security Validation Platform is unmatched in enabling an organization to focus on and remediate the exposures posing the greatest risk.
By aligning with DORA’s requirements for ICT risk management, resilience testing, incident handling, and third-party oversight, Picus ensures your team has the insights needed to address gaps effectively and efficiently. With clear prioritization and actionable recommendations, compliance becomes a seamless part of strengthening your security posture.
Discover Risk & Compliance Content









.png?width=3200&height=323&name=Pattern(1).png)
See the
Picus Security Validation Platform
Request a Demo
Submit a request and we'll share answers to your top security validation and exposure management questions.
Get Threat-ready
Simulate real-world cyber threats in minutes and see a holistic view of your security effectiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions
DORA Framework refers to the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), a regulation established by the European Union to ensure financial institutions can withstand and recover from ICT-related disruptions. It focuses on key areas such as risk management, incident response, resilience testing, third-party oversight, and information sharing.
DORA compliance ensures a unified approach to digital operational resilience, reducing risks from ICT disruptions, mitigating vulnerabilities, and fostering trust across the financial sector. It also aligns financial institutions with EU-wide security standards to protect stakeholders and maintain business continuity.
The DORA Framework shares similarities with standards such as ISO 27001, ISO 27002, ISO 27005, and ISO 22301, as it adopts many of their concepts. However, DORA is a regulation specific to the financial sector and takes precedence over other directives like NIS2 for organizations within its scope. While NIS2 applies to a broader range of entities, financial institutions covered by DORA are exempt from NIS2 compliance. Unlike GDPR, which focuses on personal data protection, DORA addresses the resilience of all ICT systems and operations.
The DORA Framework applies to a broad range of financial institutions, including banks, investment firms, insurance companies, and ICT service providers. Other covered entities include credit rating agencies, cloud service providers, and cryptocurrency firms operating in the EU.
Non-compliance with DORA can result in significant financial penalties, including fines of up to 2% of annual global turnover. Additionally, failure to comply may lead to reputational damage and operational disruptions due to unmanaged ICT risks.